Human and animal powered water lifting devices
Practical Action
Advantages
Cheaper construction than most reciprocating
suction and lift pumps
Maintenance using local skills and materials
Long piston stroke gives water delivery of up
to 90 litres/min at 4 metres depth
Disadvantages
Limited to wells of less than 7 metres in
depth
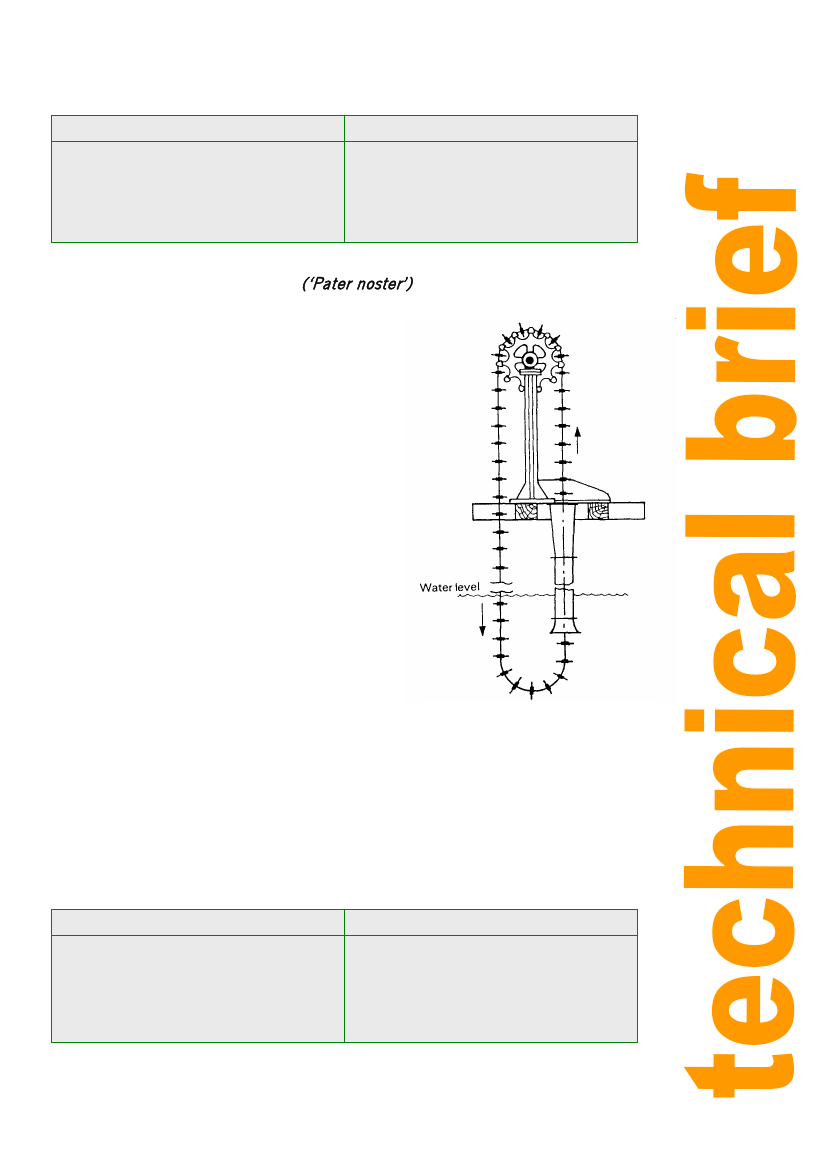
Chain / Rope and Washer Pump (‘Pater noster’)
These pumps have been used in China and Europe for
many centuries. The pump consists of an endless
chain or rope on which washers are mounted at
intervals. The endless chain usually passes over two
drums. The upper drum is above the top of well to
which axle and handle is attached for operation. The
chain with disc passes through a pipe which extends
downward from the top of well to about 0.6 to 0.9m
below the surface of water. As the chain rotates the
discs trap the water in the pipe and carry it to the
surface where it is discharged in a trough.
Although in theory it is possible to construct a vertical
chain and washer pump to raise water to any height,
most do not exceed 35 metres. At this depth the
average yield is calculated as 10 litres/ min. However,
rope pumps more commonly operate at depths of up to
10 m with a water yield of 40 litres/ min. The rope
pump can be adapted to be operated by a horse and
will raise 60 litres/min from a 20 m well.
Chain/Rope and washer pumps require less
maintenance than other equivalent pumps. Their
simple design means that repairs can often be done by
users and require few spare parts. Models can use parts
that incorporate commonly available materials such as PVC
pipe, rope, and old car parts.
Figure 12: Chain and Washer Pump
The main disadvantage of this type of pump for irrigation is that since this is not a pressurised
system it may take time to receive water from the well with the water falling back to the level
of the bottom of the well when not in use.
A variation of this design is called the "dragon-spine" pump, which lies at a shallow angle to
the horizontal. In this case, lifting height is rarely more than 6 metres. However, the design is
very flexible and can easily be adapted to circumstances.
Advantages
Relatively cheap, and easy to manufacture
(for wells down to 35 m rope pumps are five
times cheaper than piston lift pumps.)
Maintenance uses local skills and materials
Disadvantages
Operation limited to depths of up to 35 m.
Initial water delivery is relatively slow at
greater depths.
Frequent simple maintenance required
Medium to high efficiency (50-80%)
9